¡HI! If you want to propose us a project, send a mail to info@albatian.com


ALL INFORMATION ABOUT
BPM, PROCESS, R & D, TECHNOLOGY
Digital Transformation Life Cycle
By Pedro Robledo, BPM process management expert
When a company raises the Digital Transformation it encounters two main obstacles, the lack of understanding about what is Digital Transformation and not knowing how to start. The approach is already a first step, because you will have realized that you can not lose competitiveness because of your digital incompetence, and the organization is not willing to disappear in the near future if you do nothing about it.
It is important to be aware that Digital Transformation refers to the use of digital technologies to achieve new business models where the physical and digital worlds are mixed, with disruptive improvements in the organization, becoming more competitive, increasing revenues, greater efficiency and greater Customer (or citizen) satisfaction, which will produce three main changes in the organization: change in the line of products and services, change in the value chain and change in the business model.
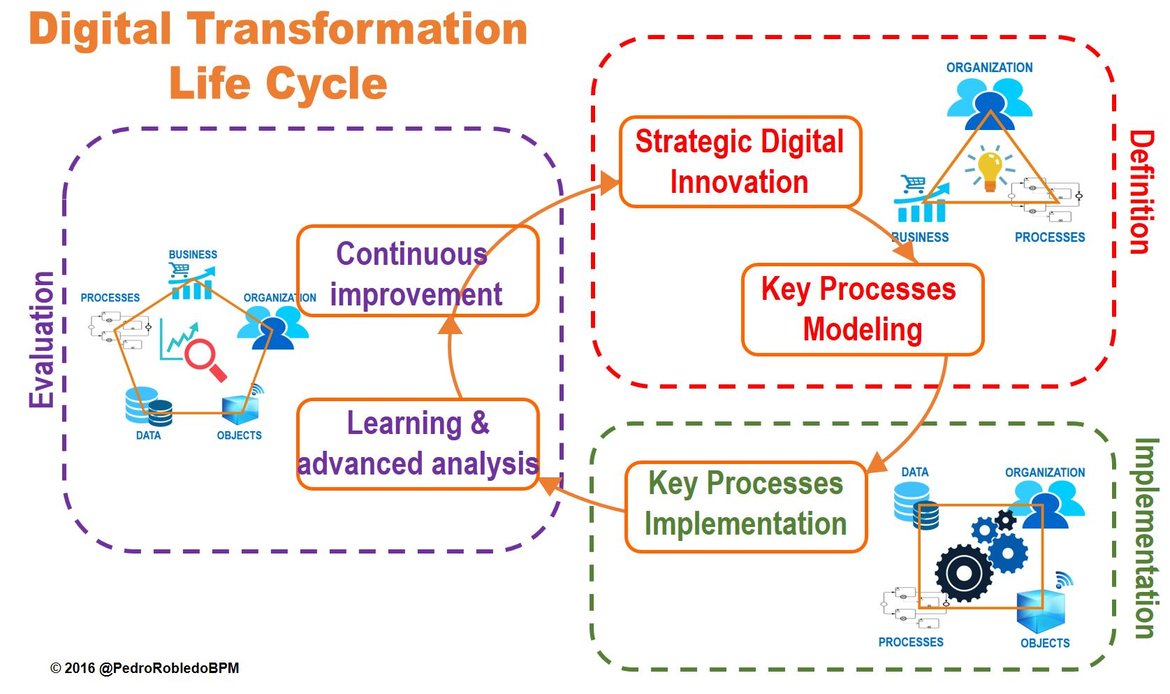
The life cycle of digital transformation represents a journey of innovation that seeks continuous excellence to respond with agility to possible global economic changes, business competition, new regulations, new technological disruptions to arrive and mainly to respond to new customer expectations. As any management it is necessary to include a first step of DEFINITION (identify the new digital business model and define the objectives or challenges to be achieved), a second dtrp of IMPLEMENTATION (execution of the new model) and a third step of EVALUATION (monitor the achievement of strategic objectives by analyzing results and observing trends).
Digital transformation must be understood as a process of permanent innovation, which we represent as a continuous cycle. Let's look in detail at each of these three main phases of the Digital Transformation life cycle:
1.- Phase of Definition of the three main changes of the new Digital Organization:
Change in the line of products and services; change in the value chain; and change of the business model. The following steps must be taken:
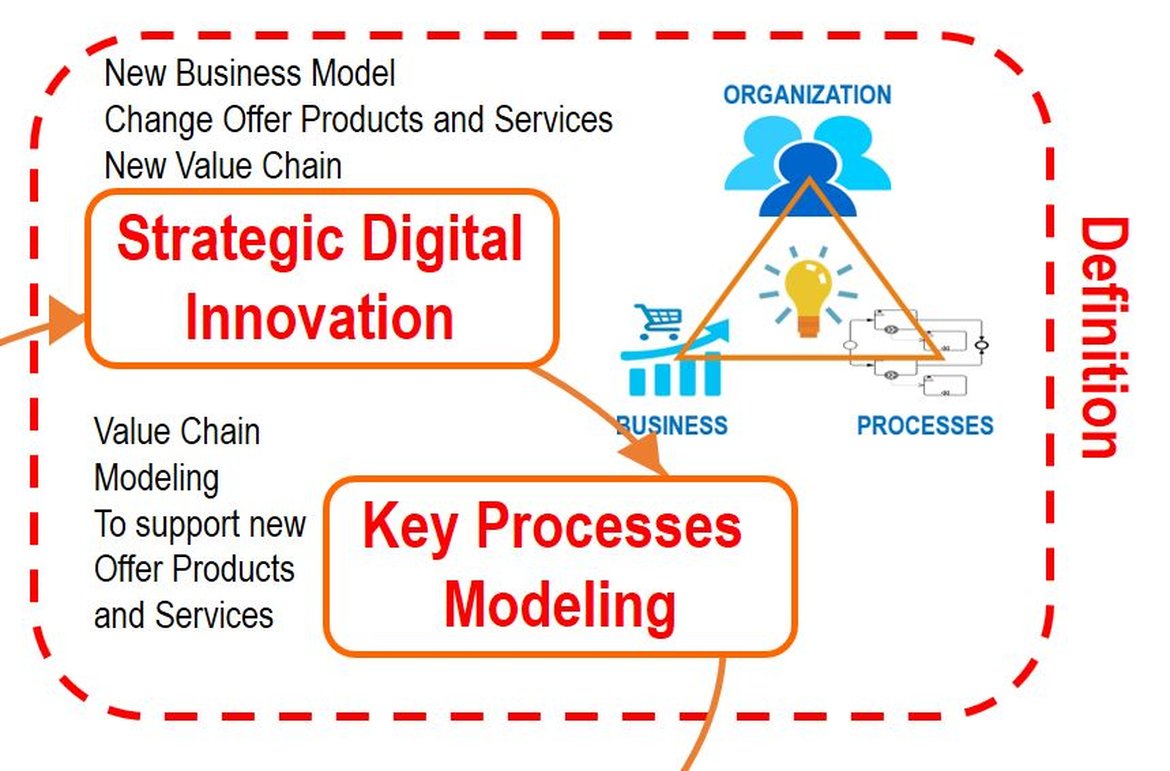
A) Strategic Digital Innovation Stage: A process that begins by understanding the strategies and objectives of the organization, completely rethinking its operations, to ensure an attractive value proposition for customers. Digital vision and business strategy are then translated to achieve digital transformation into effective structural changes by creating, communicating and improving the requirements, principles and key models that describe the future state of the organization and enable its digital evolution.
To do this, it is necessary to apply the Enterprise Architecture (EA) discipline that provides the most complete ability to arrive at a common understanding of how infrastructure and business functioning really are (strategies, operations, information systems and technologies) and thus to know with more certainty what, where, when, how, and why to digitally transform the organization. With the Enterprise Architecture is articulated the desired future digital state and its corresponding plan to achieve it, aligning strategy and tactical requirements. It defines the relationships between the three main assets of a company: Business (Strategy, Quality, Value Chain, Line of Products and Services), Organization (Functional Units, Third Parties, Locations) and Processes (Process Models, Business, Activities, Flows). This study allows identifying the key processes to adapt to new business models, and what effective changes are necessary to eliminate resources that do not contribute value (people, information systems, technology, people, intelligent objects ...).
Digital transformation implies an important change in the organizational culture, being a very critical factor of success for the efficiency and effectiveness of the transformation. The organizational change brought about leads to a change of attitude of employees, because it changes the way they do and supervise the work of their responsibility. Change challenges workers to learn, adapt, assimilate information, and reach new skills. For the change to be successful, the employee is required to be motivated, and for this, he will have to know the objectives of the change and have the tools and information necessary for his new way of working. In order to manage digital change, it will be necessary to systematically lead a parallel project that creates a climate for change, engages and empowers the entire organization, motivates those involved in change, assimilates that it is a change of improvement, and is managing to implement and maintain the transformation with short-term achievements and over time.
B) Phase of Modeling of Key Processes: With the strategic and tactical objectives defined in the Enterprise Architecture, the modernization, rationalization and simplification of the current business processes is prioritized, as well as the creation of the new key processes necessary for the new business rethinking.
BPA (Business Process Analysis) solutions identify end-to-end processes, defining business models (representation of business processes in BPMN - Business Process Model & Notation); Performing simulations on the model looking for inefficiencies, possible operating errors and inconsistencies; and analyze the factors that allow and limit the process, as well as verify that the models are aligned with the desired strategic goals and performance targets.
2.- Phase of Implementation of the Key Processes of Business:
Once you have the models of the key processes, you need to implement them, that is, the automation of business processes for execution in a BPM:Workflow engine (Business Process Management Workflow), taking into account the necessary integration with the Technologies (SMACT: Social Networks, Mobility, Analytics or BigData, Cloud and Things – Internet of Things).
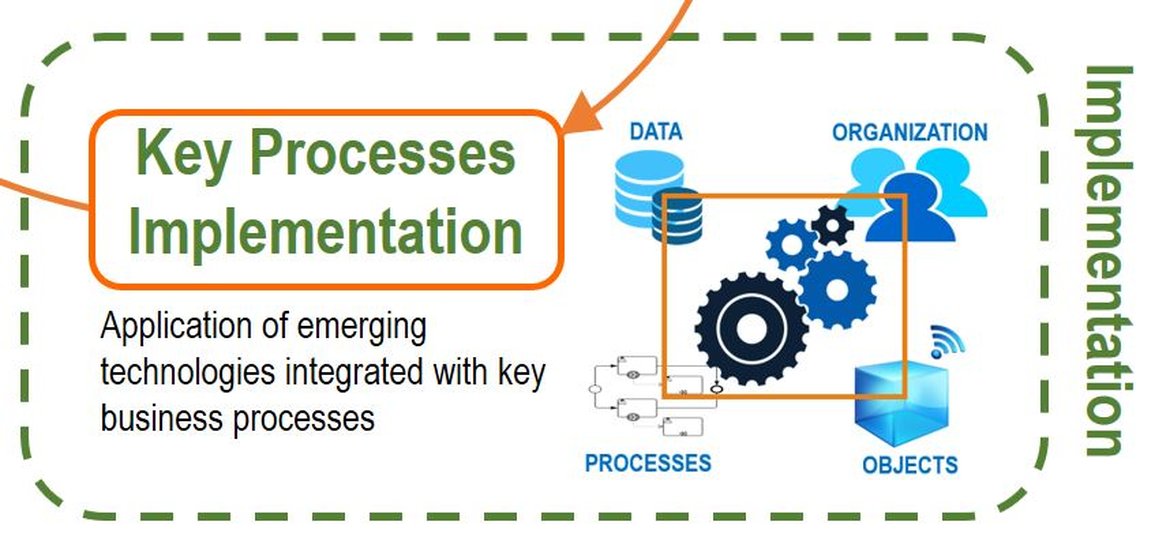
The BPM engine as an orchestrator (organizer, controller and supervisor) will be in charge of executing the different process instances (different cases of each process model) responding to all events that occur, optimally allocating all tasks in a priority way to the participants in a process to be resolved on time and seeking customer satisfaction.
Complete traceability is achieved by connecting the four main pillars in all areas of the organization: DATA (business information flowing through the process flow and the inherent information of the execution of the process instances by the BPM engine: Workflow ); OBJECTS (intelligent objects through their sensors can send or receive events to respond with an action interacting with processes); ORGANIZATION (management of the resources involved in the execution of the process, with dynamic allocation of participants according to their roles); and PROCESSES (the engine stores all relevant process flow data in order to optimally organize resources, control the execution of activities, assist in decision-making, respond to events that occur, and monitor Performance by managing metrics based on time, cost, capacity and quality).
3.- Digital Transformation Evaluation Phase for the performance management and fulfillment of objectives, with alignment to the business strategy and analysis of continuous improvement. It is performed in two stages:
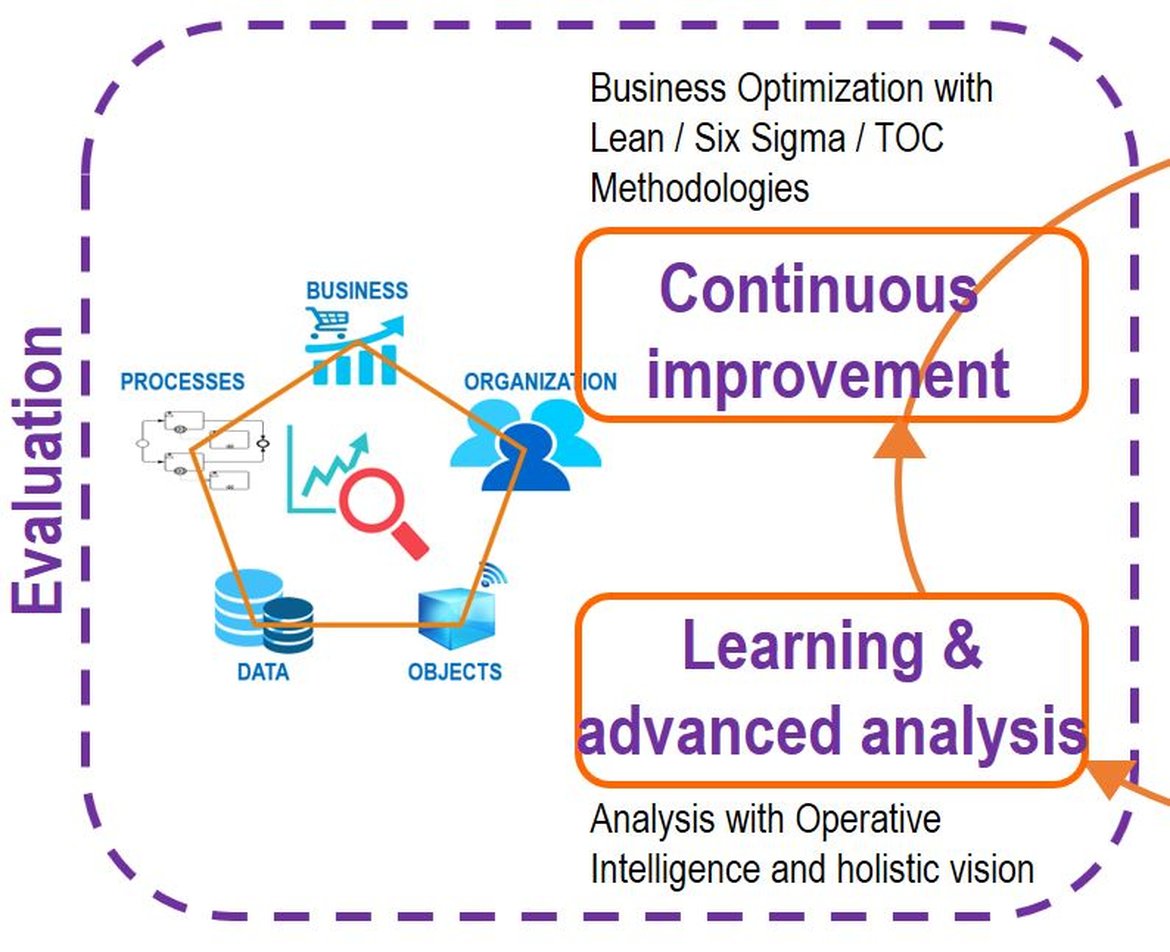
A) Stage of Learning and advanced analysis: The Digital Company must always seek operational excellence, seeking competitive innovation. In order to analyze what innovation is required, the organization has to study the current performance of the 5 main pillars (Business, Organization, Objects, Data and Processes) with precise and relevant metrics.
In the execution of the key processes that support the new business models of the Digital Company, it requires to process all the information in real time (through BAM - Business Activity Monitoring), so that it has the capacity to generate alerts or make decisions (reaction to business events or changes to be applied for continuous improvement) in a timely manner. Automatic learning through cognitive ability will support the decision-making of participants in the business process, as it will help them make better decisions based on information analysis and large volumes of data. Along with advanced analysis (Streaming Analytics with the application of CEP methodology -Complex Event Processing-) will allow the organization to anticipate to detect patterns of behavior through the correlation of events that allow you to identify potential risks in time operations or identify opportunities that require an immediate action.
It is necessary to align the performance of the key business processes that support the new digital business model to the strategic objectives, so that the time and resources necessary to improve those processes that help to achieve the strategic challenges are focused. Organizations need to be flexible, to be prepared for the different changes, but always oriented to their strategy, to align the behavior of the people towards the achievement of the defined strategic objectives. For this, the organization should be based on the methodology BSC or Balanced ScoreCard, which is based on facilitating the transformation of a company's strategy into measurable and related operational objectives, seeking the creation of value, and aligning the strategy with people, processes, resources, budget and customer satisfaction. By means of the Balanced Scorecard it makes possible the strategic learning, once tested the hypotheses of our strategies it is easy to know how to take the company to get its vision, it becomes a dynamic process of permanent feedback and if for example some external factor changes, it will allow you to be proactive and act quickly to adapt to the new circumstances.
B) Continuous Improvement Stage for Business Optimization: Given the changing and competitive environment faced by companies, it is vital to consider a methodology for continuous improvement that allows an optimized, sustainable and profitable digital business model. Three complementary methodologies stand out among themselves in the search for continuous improvement of the operations of an organization:
- Six Sigma Methodology, which focuses on providing a way forward to continuously improve the quality of the product or service, seeking: cost savings, eliminating variability and waste, increasing customer satisfaction and seeking 99.9999% of effectiveness.
- Lean Methodology, which provides a way forward to continuously improve efficiency in manufacturing processes or service delivery. To this end, it relies on the suppression within the productive process of everything that does not bring value. In this way, immediate results are achieved in productivity, competitiveness and profitability of the business.
- TOC Theory of Constraints methodology that provides a way forward to continuously improve production capacity. For this it is based on attacking the restrictions (restriction is everything that obstructs or conditions us to reach our goal) that limit the capacity of the productive processes.
RELACIONADO
-
BPM is key to the Digital Transformation
by Albatian Oct. 4, 2016
-
Process Digitalization in Digital Transformation
by Albatian Jan. 9, 2017
-
Lean+SixSigma+TOC provide methods for continuous process improvement in BPM
by Albatian Feb. 13, 2017
-
Agile, the last trend in information technology
by Albatian Feb. 19, 2017
-
Any Business Innovation and Transformation requieres an Enterprise Architecture
by Albatian March 27, 2017
-
BPM is the most effective discipline of business management
by Albatian Sept. 15, 2016
-
Not enough with an independent Management of a Process
by 4 May 9, 2017
-
How to Calculate the ROI of a BPM Initiative?
by 4 July 9, 2017